二硫化モリブデン(MoS2)は安定な2H構造と準安定な1T構造を有し、1T構造は難分解性物質の分解が可能な光触媒としての利用が期待されています。このため、1TリッチなMoS2の合成やその生成挙動に関する研究を行っています。
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) has a stable 2H structure and a metastable 1T structure, and the 1T structure is expected to be used as a photocatalyst capable of decomposing persistent substances. Research on the synthesis and its behavior of 1T-rich molybdenum disulfide is being investigated.
超臨界二酸化炭素(SCCO2)はMoS2の層構造の剥離を促進し、同時に2H相から1T相への相変化を促す効果があります。このため、各種条件下でSCCO2によるMoS2の処理実験を行い、得られたサンプルの分析、性能評価(難分解性物質の分解)などを行っています。 SCCO2の温度や圧力などを変化させることで、 2H相と1T相の存在量比率を制御できることが判明しており、今後光触媒としての応用が期待されます。
Supercritical carbon dioxide (SCCO₂) promotes the exfoliation of MoS₂ layered structures and facilitates the phase transition from 2H to 1T phase. Currently experimental treatments using SCCO₂ have been conducted on MoS₂ under various conditions. These experiments involve analyzing the obtained samples and evaluating their performance, particularly in terms of decomposing persistent substances. By varying parameters such as temperature and pressure, it has been discovered that SCCO₂ allows precise control over the ratio of 2H and 1T phases.
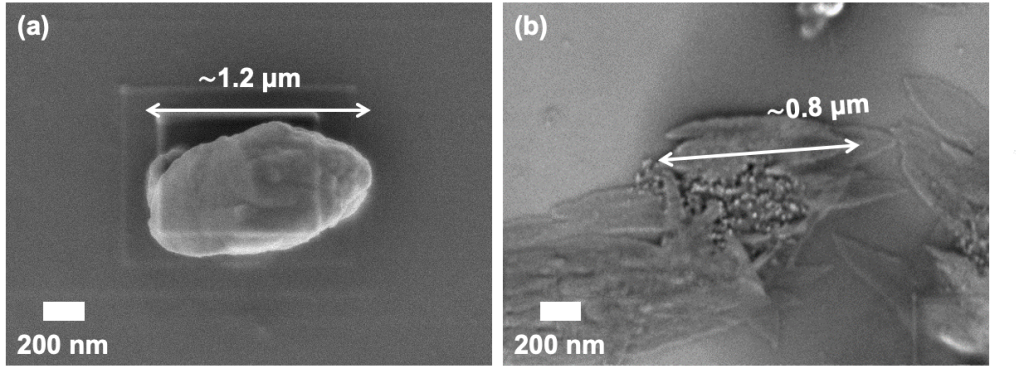
TEM images of (a) MoS2 bulk particle (b) exfoliated MoS2 nanosheet by SCCO2 assistance
関連する研究論文 Related research papers(s):
Han et al., SCF, (2024).