木質バイオマスの構成成分であるリグニンは、樹脂原料などとして工業的に重要な化学品であるBTX(ベンゼン、トルエン、キシレン)と似た構造を有しています。このため、自然由来のリグニンからBTXを生産し、従来原料として用いられてきた石油を置き換えることが期待されます。当研究室では、リグニンの変換を可能にする環境調和型の化学変換手法に関する研究を行っています。
Lignin, a constituent of woody biomass, has a structure similar to that of BTX (benzene, toluene and xylene) which are industrially important chemicals used in resins and other materials. Therefore, there is an expectation to produce benzenes from naturally derived lignin, replacing conventional petroleum-based feedstocks. In our research group, we are currently studying environmentally friendly chemical conversion methods that enable lignin transformation.
Sustainable supply of biomass-based BTX
リグニンの変換には、リグニン中に存在するエーテル(C-O)結合の開裂が重要です。エーテル結合に水素を付加する反応(水素化分解)がリグニンの分解に有効であることが知られており、モデル物質(ジェフェニルエーテル)を用いた分解挙動の検討や反応速度論を用いた解析を行なっています。
The cleavage of ether (C-O) bonds present in lignin is crucial for its conversion. The reaction of adding hydrogen to ether bonds, hydrogenolysis, is known to be effective for lignin decomposition. Investigation on the decomposition behavior using model compounds (diphenylether) and analyze reaction kinetics are ongoing.
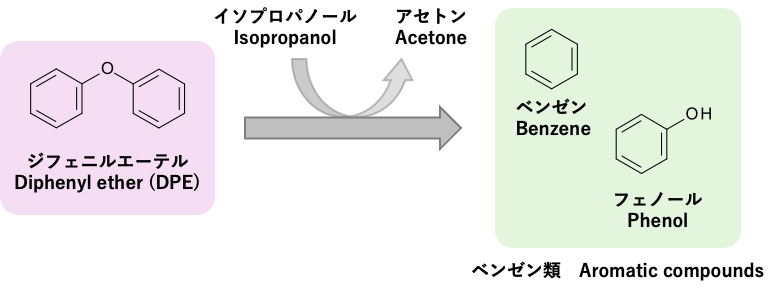
Transfer hydrogenolysis of DPE
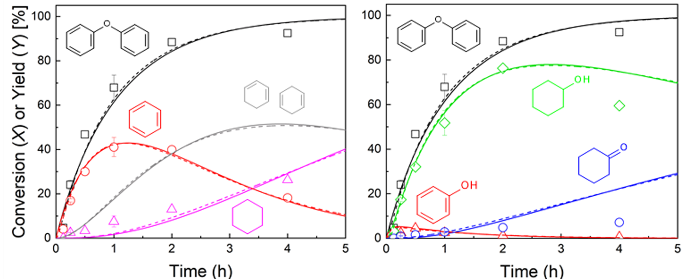
Behavior of DPE conversion to benzene, phenol and derivatives
関連する研究論文 Related research papers(s):
Dowaki et al., IECR, (2024).